Did you know that there are other types of Social Security benefits beyond retirement benefits? Social Security offers five major types of benefits: retirement, family, survivors, disability, and supplemental security income. In this article, I will be reviewing family benefits.
Social Security Family Benefits
Family benefits are often referred to as “spousal” or “child” benefits. If a worker is receiving Social Security retirement benefits or Social Security disability insurance (SSDI), some family members may also be eligible to receive family benefits on that worker’s earnings record. Eligibility for family members depends on specific family circumstances.
Primary Insurance Amount (PIA)
Your Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) is a significant figure as it relates to your family’s Social Security benefits. Unfortunately, you will not be able to find this precise figure when logging into your Social Security account. The calculation of this amount is complex! You must begin by calculating your Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME). Rick Miller outlined how to calculate your AIME in his article here. Then, you can use your AIME to calculate your PIA using the formula and details outlined in my previous article here.
What members are eligible and under what circumstances?
As a reminder, the worker must have already filed for retirement benefits or disability benefits before any family members are eligible for benefits. The additional requirements surrounding age and circumstances are outlined below:
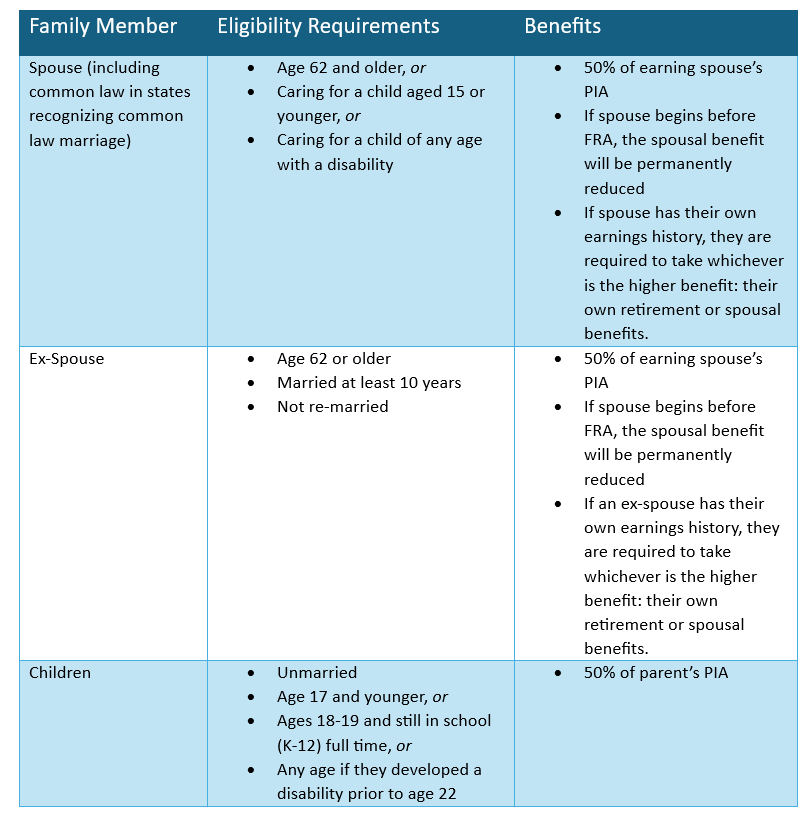
This list of eligible family members may surprise you! Some clients were surprised to learn that they can receive Social Security benefits on their spouse’s record, even if they do not have an earnings record of their own. Additionally, several clients did not realize that there are benefits for disabled adult children and parental caretakers of disabled children.
Beyond the family members listed above there may also be limited circumstances for married children, stepchildren, adopted children, grandchildren, or step grandchildren to be eligible for family benefits.
Family Maximum
With all these family members in mind, Social Security does limit the total amount of benefits a family can receive on one worker’s earnings record. This is known as the family maximum. The family maximum is based on the worker’s PIA and therefore their history of earnings.
There are two different calculations for the family maximum dependent on whether the worker has filed for retirement benefits or disability benefits.
Like the PIA formula, the family maximum formula pertaining to a worker filing for retirement benefits contains a few bend points whose amounts depend on when the worker turned 62.
For 2025, these bend points are:
- The first $1,567
- The amount between $1,567 and $2,262
- The amount between $2,262 and $2,950
- The amount over $2,950
For a worker turning 62 in 2025 filing for retirement benefits, here is the family maximum formula:
150% of the first $1,567 of PIA
+
272% of PIA between $1,567 and $2,262
+
134% of PIA between $2,262 and $2,950
+
175% of PIA above $2,950
The family of a worker that has filed for disability benefits has a completely different family maximum. At most they are eligible to receive 85% of the worker’s AIME. However, this family maximum is further defined as an amount that cannot be less than the worker’s PIA or more than 150% of the worker’s PIA.
Example: Social Security Family Benefits Calculation for a Retired Worker
The worker’s PIA is $3,285.90.
150% of the first $1,567 = $2,350.50
+
272% of ($1,567 – $2,262) = $1,890.40
+
134% of ($2,262 – $2,950) = $921.92
+
175% of PIA above $2,950 = $587.83
Total: $5,750.65 (which gets rounded down to $5,750.60) family maximum
The benefits paid to the worker are not counted in the family maximum.
One additional exception is that benefits paid to an ex-spouse(s) are not counted as part of the family maximum.
What happens if your implied family benefits are higher than the family maximum?
If the calculated family benefits exceed the family maximum, then the benefits of each family member (other than the worker) decrease proportionally until you reach the family maximum.
What is the impact on family benefits if a worker delays retirement benefits past full retirement age?
If a worker decides to delay their own retirement benefits past their full retirement age to earn delayed retirement credits that does not automatically increase their family’s benefits. Family benefits do not earn the same delayed credits.
The family benefits would only increase if,
- The worker was earning enough to increase their PIA (because that is a primary factor in the family benefits calculations), or
- If a spouse filing for spousal benefits was closer or at their full retirement age (therefore they would receive less of a reduction in benefits).
Just because you and your family are eligible to receive benefits at a certain time, doesn’t mean that is when you should claim them. For advice on your family’s best Social Security claiming strategy, consult your Sensible team.
Future articles will discuss Social Security survivors, disability, and supplemental security income benefits.
Photo by Johnny Cohen on Unsplash